4Nids.com – In terms of architectural design, passive design is a set of strategies that incorporate the use of natural energy sources to reduce a building’s energy consumption. Passive design architecture takes advantage of natural elements such as siting, form, detailing, and construction assemblies. By reducing energy consumption, a building can use less electricity, downsize its HVAC equipment, or eliminate it completely. This method shifts the first cost to the enclosure. But it requires careful planning and education of occupants.
Passive design architecture emphasizes aesthetic appeal and is less complicated
In terms of building construction, most devices are either passive or active. Active design refers to devices with mechanical or electrical components that require electricity. Passive design architecture, on the other hand, has no mechanical components. Passive design architecture emphasizes aesthetic appeal and is less complicated than its active counterpart. Most passive designs are low-maintenance and often contain no moving parts. However, electrical components may require frequent maintenance and can increase operational costs and environmental impact.
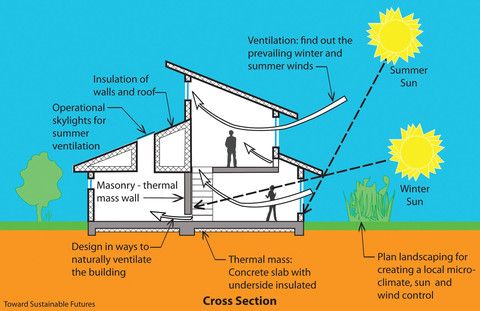
In addition to minimizing energy consumption, passive design architecture helps to prevent air pollution. By using continuous insulation, this design also ensures that the building is not susceptible to thermal bridging. Moreover, it should be airtight, to prevent air infiltration and loss of conditioned air. High-performance windows and doors should be installed to keep the building envelope airtight. Passive design architecture should use balanced heat and moisture-recovery ventilation, and use minimal space conditioning systems.
Rooms facing east are perfect for the kitchen

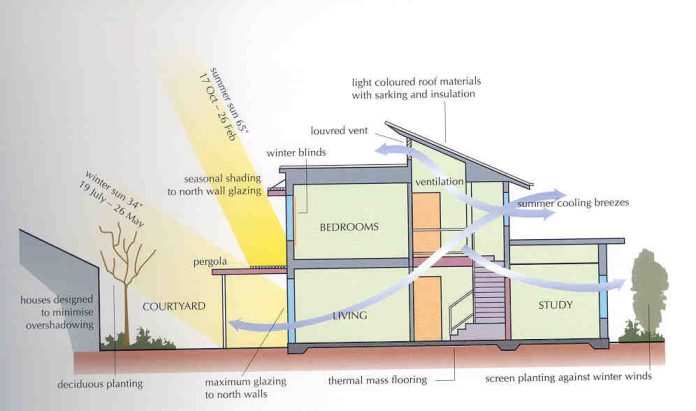
Passive design also uses exterior shading techniques to keep occupants comfortable during the day. Ideally, the main living areas should face the north. This will ensure all-day sunshine, although it may need some horizontal shading in the summer. In winter, the sun’s warmth will be stored in thermal mass. East-facing rooms are excellent for kitchens as they receive good morning light and solar gain. East-facing rooms also benefit from cool afternoons.
Passive design architecture maximizes solar gain and minimizes energy usage
Passive design architecture is a method of designing buildings that maximize energy efficiency and human comfort. This approach is applied to homes, office buildings, and high-rise buildings. Its key features include continuous insulation, airtight envelope, highly insulated windows, and heat recovery from ventilation. Additionally, passive design architecture maximizes solar gain and minimizes energy use. In short, passive design architecture saves money and creates a comfortable interior environment.
To make passive houses brighter and more welcoming, five architects are pushing the boundaries. Samantha Daly of Dwell wrote a recent article on New York architecture firm Baxt Ingui Architects. The firm, which designed the 78 Third Place residential building in Manhattan, is a pioneer in passive housing. The practice has been a leader in design for over 40 years. So, what are the key elements of a passive house?
This natural air helps to regulate the internal temperature and humidity

The key to a passive design home is to replace stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. This natural air helps regulate internal temperatures and humidity. It also allows natural daylight into the interiors. To achieve this, passive design architects use cross ventilation strategies. This involves openings in opposite orientations to allow air to flow. Double spaces and atriums are other passive design architecture techniques used to encourage natural ventilation. The goal is to minimize the use of mechanical systems by as much as possible.
Passive design architecture must be suitable for each climate zone
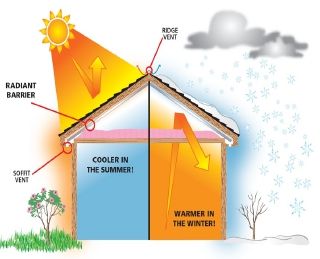
The location of a house also plays a key role in the design of passive houses. Different climate zones have different design responses. For example, Australia has eight distinct climate zones, each with its own unique climatic characteristics. As such, passive design architecture should be appropriate for each climate zone. If a building is located in an extreme climate zone, it is best not to use passive design architecture. In these instances, a passive house is less likely to have problems with heat and humidity.
The performance of a PHIUS+ building is significantly better than a traditional code-compliant structure. These houses have significantly lower heating and cooling energy bills compared to traditional structures. These buildings are also more efficient and sustainable than buildings built with code-compliant construction. The WUFI Passive climate modeling tool and a moisture and energy-modeling tool ensure that each building is optimized to achieve its full potential. However, the standards used to calculate energy consumption are different.