4Nids.com – There are many different types of infections, but one thing is constant – they all cause pain and discomfort. There are two basic types of infections: primary infections and secondary infections. While the former type of infection is a standalone disease, a secondary infection is an infection caused by a different disease. Infection symptoms vary by body part. General symptoms of infection include coughing, fatigue, rash, and pain or swelling of a joint. Your doctor will also want to determine what part of the body is affected by infection, in order to properly diagnose the condition and prescribe a treatment.
Coughs and sneezes can spread infection

If you have any of these symptoms, you may have a serious infection. Infection symptoms may include fever and chills, and some even involve respiratory organs. Coughing and sneezing can spread infection, so always use tissues to cover your mouth. In addition, hand washing is essential, as bacteria can multiply in the hands and spread through coughing. While coughing, try to practice deep breathing to protect your lungs from infection. Chest postural drainage, such as chest physiotherapy, can be helpful in loosening up mucus.
An infection can be caused by various pathogens, some of which have a minor effect on the human body, and others can cause more serious symptoms. While some infections are treatable, others require medical attention and are life-threatening. In some cases, antibiotics may not be enough to cure a condition. In any case, it is important to consult with a medical professional if you have persistent symptoms or persistent pain. If you have persistent symptoms, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
The body’s immune response to infection leads to widespread inflammation and organ failure

Sepsis is a serious medical condition that occurs after an infection in the blood. The body’s immune response to an infection results in widespread inflammation and organ failure. While antibiotics can help treat the symptoms, sepsis can be fatal if the infection is not detected in time. The first thing to do is get yourself checked out. The doctor will examine you to confirm your diagnosis and prescribe a treatment. If the infection has gotten worse, he or she may even give you intravenous antibiotics to cure it.
The most common symptoms of infection are coughing and a runny nose. A runny nose may be caused by bronchiolitis. Coughing and wheezing are common symptoms of the common cold, while croup is caused by an infection in the middle ear. Coughing may also be a symptom of a sinus or ear infection. In addition, a sore throat can be caused by a virus or bacterial infection.
Sputum may reveal an infection in the lungs
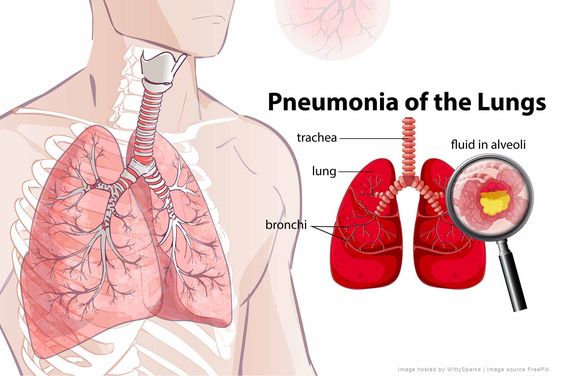
If you suspect that you have an infection, your healthcare provider may perform a physical exam to rule out other possible conditions. During this visit, your doctor will examine your ears, nose, throat, chest, and breathing. He or she may also perform a lung function test. Sputum can also reveal the presence of phlegm in the lungs, which can confirm infection. A sneeze can also send germ-filled droplets into the air, and other people may breathe in these particles.
If you experience severe diarrhea and abdominal cramps, you should see a doctor. Bloody stools or diarrhea are symptoms of other illnesses, so be sure to consult your primary care provider for further evaluation. Other causes of diarrhea can include malabsorption, certain drugs, and inflammatory bowel disease. Additional testing may be needed to identify the cause. So, it’s best to seek medical attention if your symptoms persist. If you have diarrhea, contact your doctor right away.
Apply Neosporin to help prevent the entry of bacteria

An infection can be easily spread between people. This is why you should wash your hands after using the bathroom, and don’t touch your food with unwashed hands. Similarly, you should change your dressings regularly. If your wound is fresh, you can apply Neosporin to help prevent bacteria from entering it. However, always ensure that you wash your hands properly to prevent bacteria from entering your wound. Aside from washing, you should keep your body moisturized and clean.
Regardless of the cause, pneumonia is a common lung infection. It can affect anyone, including those with COPD or asthma. It typically gets better on its own without medical treatment, but it’s important to see a doctor if your symptoms persist or worsen. In addition, people with chronic lung conditions are more likely to experience more serious complications. While the majority of infections are relatively mild, long-term lung conditions can make it necessary to see a doctor right away.